This is the German Healthcare Market
Germany’s healthcare market is No. 1 in Europe by market volume, number of patients, medical technology manufacturers, and healthcare providers.
The healthcare market in numbers
Healthcare spending in Germany exceeded EUR 457 billion in 2021, not including expenditure for wellness and fitness. The market has grown at a rate of 5.4 percent over the past five years. With 7.7 million employees and exports in excess of EUR 158 billion, healthcare is one of the largest economic sectors in Germany.
Healthcare expenditure (by OECD definition) | EUR 457 billion |
Annual market growth (CAGR 2016-2021) | 5.4 percent |
Employment | 7.7 million |
Exports | EUR 158 billion |
Imports | EUR 145 billion |
Number of companies |
|
| Source: Destatis, BMWK, BVMed 2023 | |
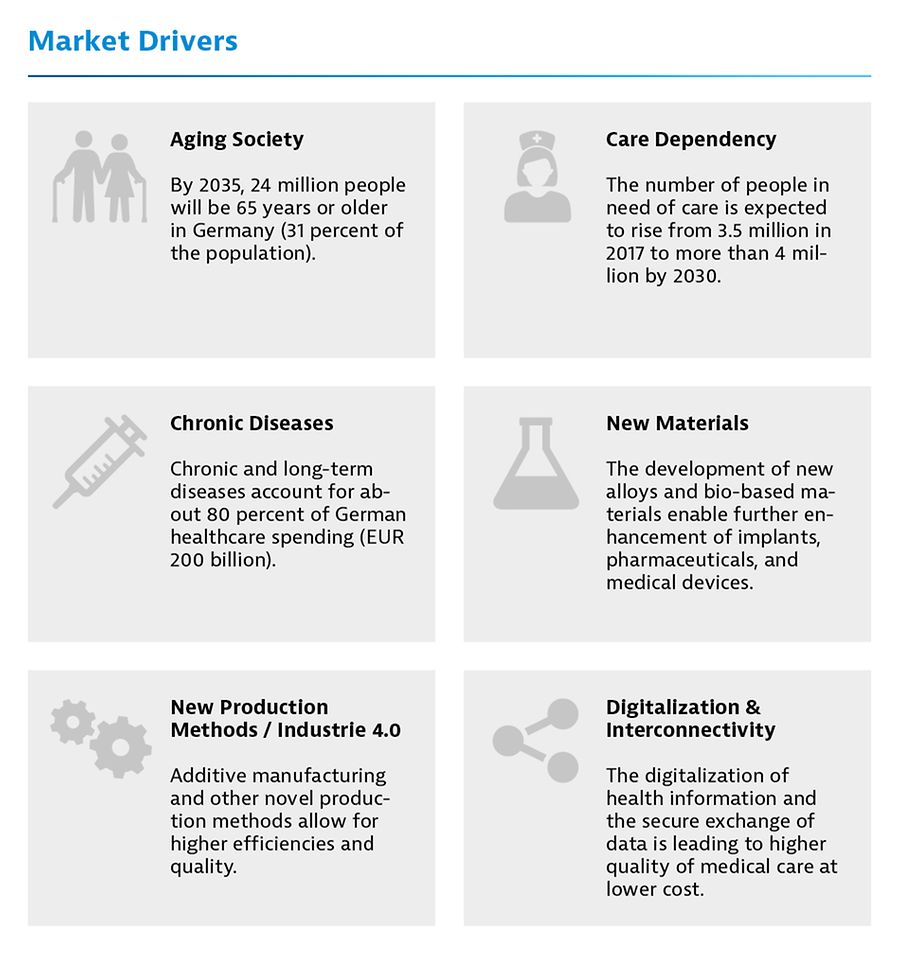
This drives the market
(Almost) universal health insurance coverage
Health insurance coverage is mandatory in Germany. Insurance premiums are shared by employers and employees. The vast majority of the population is enrolled in public health insurance plans. About ten percent choose private providers. Both publicly and privately insured can choose their provider. Currently, there are 96 public and 41 private health insurance companies operating in Germany (2023).
Inpatient care in Germany
More than 1,800 hospitals with nearly 500,000 beds operate in Germany – not including rehabilitation or elderly care facilities. The overall number of medical hospitals is declining as smaller general hospitals close or merge with other hospitals to increase efficiency.
The share of privately operated hospitals continues to rise
The share of privately operated hospitals continues to rise | © German Hospital Federation 2017Innovation clusters as key to success
Every year companies participate in thousands of research projects with other partners from industry and scientific institutions, emphasizing Germany’s reputation as a leading environment for healthcare and life sciences. Along the entire value chain – from R&D through scale-up and production to sales and marketing – Germany is known for its outstanding capabilities, resources, and infrastructure.
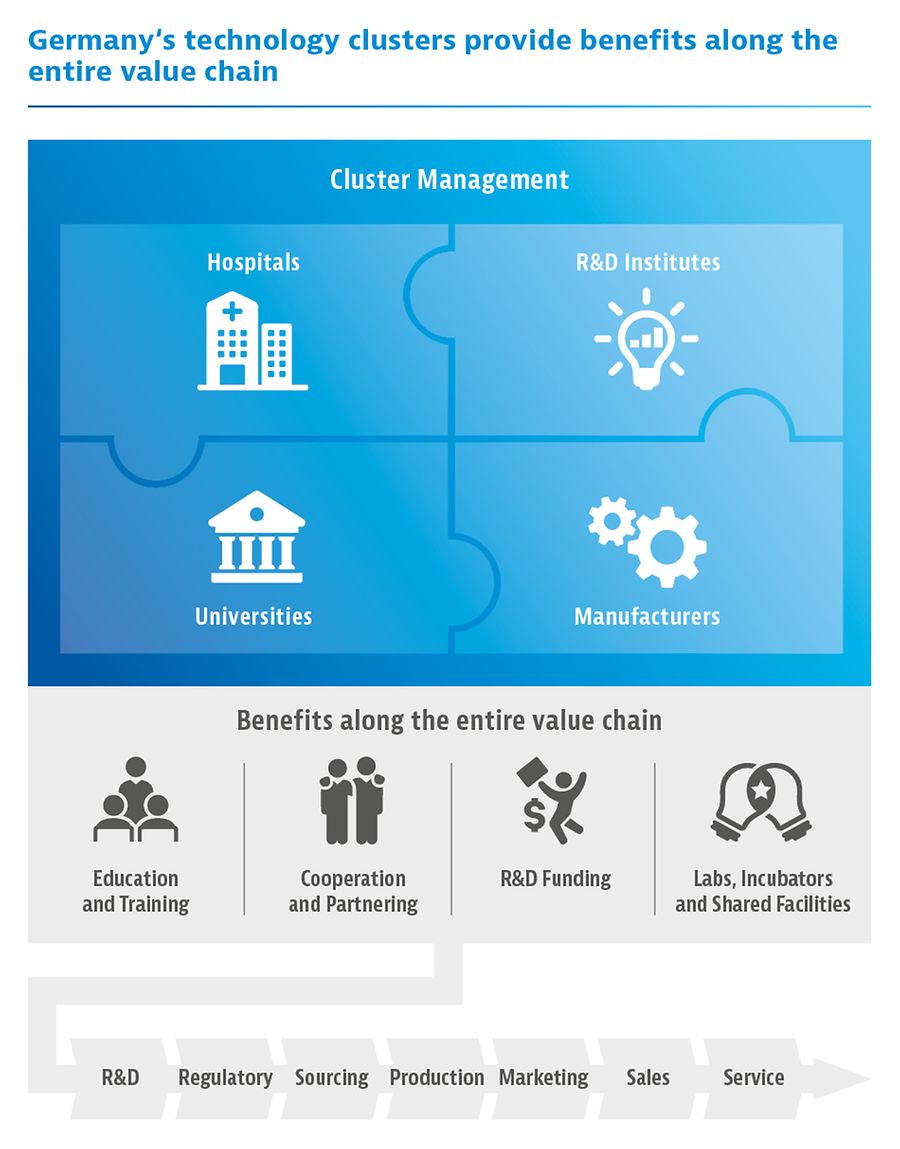
Medical Technology Clusters and BioRegions
Germany is home to more than 30 specialized cluster networks focusing on medical technology. Dedicated cluster management teams help obtain funding for joint R&D projects, provide shared facilities, and organize educational training programs for their members.
Germany’s “BioRegions” are regional initiatives for the advancement of modern biotechnology. Over the past three decades, these biotechnology clusters have developed to become Europe’s leading R&D hubs. Each region specializes in particular areas and facilitates collaboration between universities, R&D institutes, and private sector companies.
